20% of people’s foot issues are due to onychocryptosis, as is known in the medical community. People between the ages of 10 and 20 as well as those in their 50s and 60s are frequently affected.
It’s most likely an ingrown toenail if you’ve had discomfort or swelling in your toes. In addition to being painful, it can be quite uncomfortable.
You will learn everything you need to know from this article. We’ve got you covered on everything from the causes of it, to how to prevent them and even how to attend to them at home.
Table of Contents
What Causes Ingrown Toenails?
1. Fungal contamination
Athletes’ foot and other nail fungus infections will thicken the nail and increase its propensity to penetrate the epidermis.
2. Wrong Cutting of Nails
This growth might happen if your nails are improperly clipped or trimmed. For instance, trimming them too short or making the edge circular rather than straight across might cause them to grow which may cause discomfort.
3. Small Shoes/Footwear
Ingrown nails may develop as a result of wearing small footwear like shoes, or socks that are too tight. They tend to cause discomfort if pressed against them.
4. Trauma or Injury
You could accidentally hit your toes, have large objects fall on them or have other types of trauma. As a result, the nail of your toes may begin to grow into your skin resulting in this disorder.
5. Genetics
Genes may play a role in certain people’s increased susceptibility to this growth. In some circumstances, the toe structure or the nail’s shape may increase the likelihood that it may grow into your skin.
Ingrown Toenails Symptoms
- Overgrowth of your tissue: A tiny bulge or protrusion may occasionally emerge as a result of the skin around the nail growing excessively.
- Discomfort and pain: The skin around where the nail is located becomes sore, tender, or painful.
- Becomes red and starts to swell: Most often, the skin around your nail may start to swell or become red and inflamed.
- Numbness and tingling: Some people may suffer numbness or tingling in the afflicted area when the nail pierces the skin.
- Infection: Pus or discharge may emerge when it becomes infected especially around damaged areas. Infections usually worsen this condition around the vicinity of the nail growth.
- Difficulty wearing your footwear: It could get harder to wear socks or shoes as the condition worsens, especially if they put pressure on the exact area.
Risks Associated With Ingrown Toenails
If left without giving the right attention it may lead to several complications, like:
1. Cellulitis
It is a bacterial skin infection that can spread quickly and result in swelling, and redness around the affected area may result from the infection spreading past the toe. To avoid complications, cellulitis needs to be treated right away by a doctor.
2. Infection
Little skin tears caused by this disorder can let bacteria in and cause an illness. An infected nail is sometimes excruciatingly painful other times, it can cause pus or discharge, and may need antibiotic treatment.
3. Poor Mobility
When this development is extreme, it may be difficult or even impossible to walk or wear shoes comfortably, which substantially impacts a person’s quality of life.
4. Abscess
An accumulation of pus that develops into a medical condition over time is known as an abscess. An abscess may develop from an infected nail in some circumstances, necessitating surgical draining in other cases.
5. Nail Deformity
An irregular growth pattern brought on by an ingrown nail can result in twisted or malformed growth.
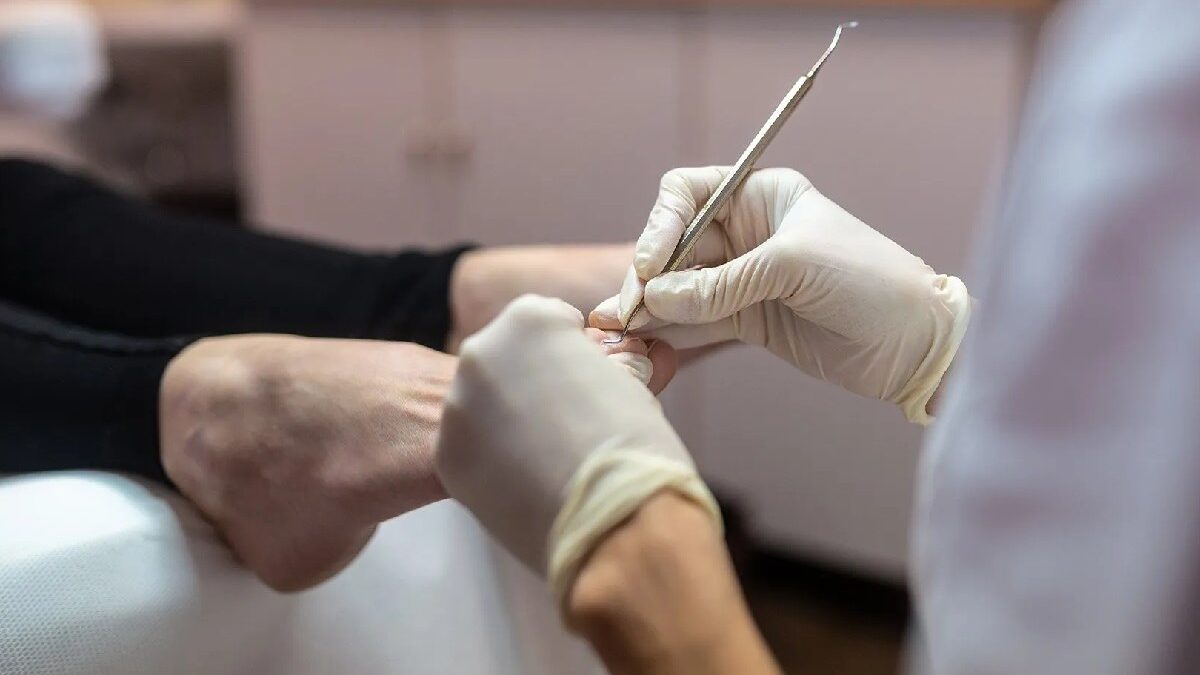
How To Remove
To successfully treat an ingrown toenail at home, you may be required to use an ingrown toenail file. Otherwise, it will lead to bleeding and further complications.

The best call to action is to immediately visit a podiatrist or healthcare professional who can safely and effectively remove the nail growth.
The treatment for this health condition typically involves the following steps:
- Soaking the foot: A 15-20 minute soaking of your toes in warm water will help to reduce edema and soften the nail and skin around it.
- Lifting the nail: When the nail has finished soaking, a doctor or podiatrist could gently raise it and tuck a piece of cotton or dental floss below it to assist it to push through the skin.
- Trimming: The medical professional may clip the nail’s edge after it has been pulled to stop it from growing back into your skin.
- Antibiotics: Your doctor may recommend antibiotics drugs to help you tackle this illness if the toenail is infected.
- Surgery: In extreme circumstances, surgery may be required to remove the nail in its entirety or part, along with the underlying tissue. This is normally carried out at a doctor’s office while the patient is under local anesthetic.
It’s crucial to keep the affected foot clean after treatment. To stop this growth from returning, be careful to adhere to the doctor’s recommendations.
In some instances, regular cutting or a change in footwear may be required to stop further development.
Conclusion
If unattended, this disease may worsen and result in the consequences of an infection or abscess. It’s critical to seek medical assistance from a healthcare professional or a podiatrist whenever you experience any of the aforementioned symptoms. Finding reliable information on how to avoid this problem is crucial.